티스토리 뷰
Spring Advanced : Rest + Security + Data JPA 로그인, 회원가입 기능이 포함된 CRUD서비스 작성하기
Korean Eagle 2020. 5. 25. 16:350. 이 포스트는 예전부터 사골처럼 포스팅에 계속 사용했던 Customer CRUD에 보안을 추가하여 클라이언트 연동까지 하는 프로그램이다. 스프링 부트로 하면 훨씬 간단하지만, 스프링 5를 그냥 사용할 때는 스프링 부트가 해주는 기본 설정 을 일일히 등록해 주어야 한다.
1. 이 포스트의 내용은 Spring Security가 설정된 REST API 서비스를 만드는 것이고 다음 포스트는 이 서비스를 사용하는 REST Client를 작성하는 것이다. 이 서비스는 회원인증, 가입기능을 포함하고 있으며, 클라이언트에서 회원가입, 로그인 기능을 지원한다. 따라서 세션관리 역시 클라이언트에서 구연할 것이다.
2. 이 서비스의 기능은 로그인과 회원가입이 포함된 CRUD기능의 구현이다.
3. 프로그램 작성절차는
3-0 데이터베이스 생성하기
3-1 Spring Starter Project로 프로젝트를 생성
3-2 dependency 추가하기
3-3 보안 서비스 설정하기
3-4 Entity 설정하기
3-5 Respository 구현하기
3-6 Service 구현하기
3-7 Controller 구현하기
4. 데이터베이스 생성하기
4-1 customers는 데이터 클래스이고 나머지는 인증관련 테이블이다.

5. 프로젝트 생성하기
5-1 이 서비스는 REST와 데이터베이스를 사용하기 때문에 Spring Web, Spring Security, Spirng Data JPA는 필수이다.
5-2 Actuator는 logging level이 debug의 경우 LSP관련 에러가 미친듯이 나오기 때문에 그냥 추가했다. 의미는 없다.
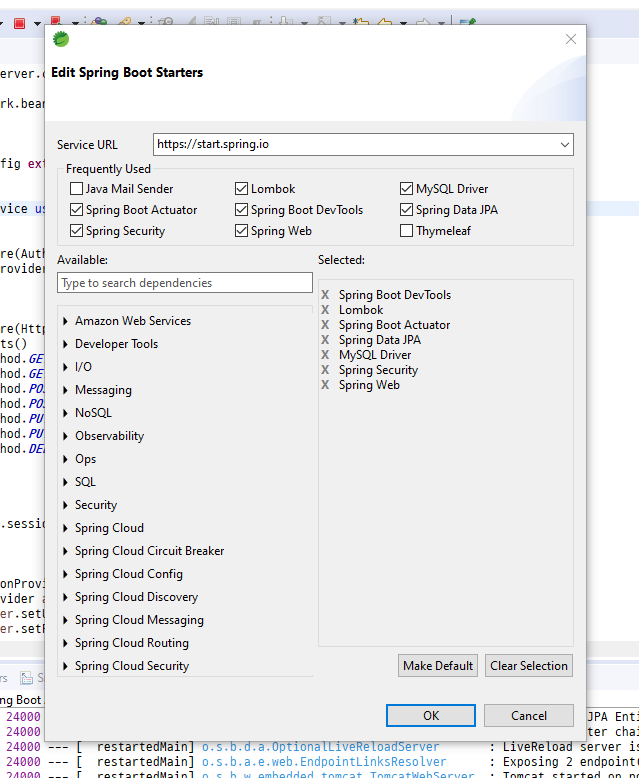
6. 보안설정하기
6-0 스프링 Security는 기본적으로 2개의 클래스를 필요로 한다 . 설정클래스와 웹보안초기화 클래스이다.
6-1 둘 중에 하나라도 없으면 정상적으로 동작하지 않기 때문에 그냥 습관적으로 추가하는 것이 좋다.
6-2 SecurityWebApplicationInitializer 클래스 생성
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.security;
import org.springframework.security.web.context.AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer;
public class WebSecurityInitializer extends AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer {
}
6-3 보안설정 클래스 생성
6-3-0 페이지 기능에 따라 접근권한을 지정하고 있다.
6-3-0-1 /api/login은 전체 open되어 있다.
6-3-0-2 이 url의 용도는 클라이언트에서 로그인 한 유저의 정보를 받아 클라언트에서 세션을 관리하기 위함이다.
6-3-1 기본 보안 정책으로 HttpBasic을 사용하고 있다.
6-3-1-1 즉 모든 요청에 인증정보를 포함하여 요청해야 한다.
6-3-2 REST이므로 상태가 없는(stateless) 서비스를 제공한다. 세션관리는 클라이언트의 몫이다.
6-3-3 로그인, 즉 인증 방법은 DaoAuthenticationProvider를 통한 사용자 임의 스키마를 통한 로그인이다.
6-3-3-1 DaoAuthenticationProvider도 사용하지 않고 그냥 Security login을 구현하고 싶으면 아래 링크를 참조한다.
Spring Advanced : Spring Boot + Security login custom 메소드로 구현하기
1. 이 포스트는 Spirng Security를 사용하지만, Security filters 로그인을 맡기는 것이 아닌 직접 코딩하는 내용이다. 1-1 보통 WebSecurity Config파일이 configure로 AuthenticationMangerBuilder를 통하여 접..
kogle.tistory.com
6-3-4 REST 서비스이기 때문에 사용자 로그인 실패에 따른 정보를 HTML대신에 JSON으로 변경해 주어야 한다.
6-3-4-1 이를 위해서 CustomeBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint를 생성하고 등록하였다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/login").permitAll()
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/api/customers").hasRole("EMPLOYEE")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/api/customers/**").hasRole("EMPLOYEE")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/api/customers").hasAnyRole("MANAGER", "ADMIN")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/api/customers/**").hasAnyRole("MANAGER", "ADMIN")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.PUT, "/api/customers").hasAnyRole("MANAGER", "ADMIN")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.PUT, "/api/customers/**").hasAnyRole("MANAGER", "ADMIN")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.DELETE, "/api/customers/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.and()
.httpBasic().authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint())
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
}
@Bean
public DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider() {
DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
authenticationProvider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);
authenticationProvider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
return authenticationProvider;
}
@Bean
public CustomeBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint() {
return new CustomeBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint();
}
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
6-3-4-2 CustomeBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint 클래스이다. 이에 대한 자세한 설명은 아래 링크 참조
Spring : WEB + Security - Basic Authentication Entry point 설정(인증 실패 메시지 변경)
1. Basic Authentication ? 1-1 웹인증에 사용되는 로그인이나 세션 검증 같은 기술들은 웹브라우저를 사용하지 않는 경우에는 적합하지 않다. 1-2 그리고 한 서버가 다른 서버의 서비스를 사용하는 경우
kogle.tistory.com
6-3-5 위의 보안설정 클래스에서 사용한 EntryPoint 클래스 코드이다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.security;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint;
public class CustomeBasicAuthenticationEntryPoint extends BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException)
throws IOException {
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
response.addHeader("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=" + super.getRealmName() + "");
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("HTTP Status 401 - " + authException.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
super.setRealmName("pilseong");
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
7. 이제 데이터베이스의 Entity를 설정해야 한다.
7-1 현재 4개의 테이블을 사용하고 있지만 하나는 연계테이블이므로 3개의 Entity를 생성해야 한다.
7-2 Customer Entity 클래스 생성
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@Entity
@Table(name = "customers")
public class Customer {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
private String email;
}
7-3 User Entity 클래스 생성
7-3-1 Role과 Many to Many 관계다. 설정에 주의한다.
7-3-2 Many to Many의 관계의 경우 REST 서비스를 위해 DTO를 생성해야 한다.
7-3-2-1 그냥 Entity를 사용할 경우는 서로 참조하기 때문에 Json생성시 무한 반복된다.
7-3-2-2 이 문제는 아주 중요한 이슈 중 하나인데 5가지 해결책이 있다. 여기서는 자체해결하는 방법이다.
7-3-2-2-1 이 문제에 대한 포스트는 아래 링크를 참조한다.
Hibernate Basic : Bi-directional 관계 Entity의 JSON 재귀적 호출 해결
1. 이 포스트는 하이버네이트의 양방향 One to Many나 Many to Many관계에서 발생하는 무한재귀호출에 대한 것이다. 2. 이 문제는 jackson이 객체를 네트워크로 보낼 데이터로 변환(serialization)하면서 circle
kogle.tistory.com
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.JoinTable;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column
private String username;
@Column
private String password;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column
private String email;
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(name = "users_roles",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "user_id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "role_id")
)
private List<Role> roles;
}
7-3-2-2 위에 언급했듯 Recursion문제 해결과 클라이언트 구현 편의성을 위해 UserDTO 생성한다.
7-3-2-2-1 중요한 부분은 Role 객체 대신 Role의 이름만 포함한다. 그렇게 해야 Recusive가 발생하지 않는다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.dto;
import java.util.List;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class UserDTO {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private List<String> roles;
}
7-4 Role Entity 클래스 생성
7-4-1 User과 Many To Many 관계임에 신경쓴다.
7-4-2 User와 Recusive관계가 있기 때문에 @Data를 사용하지 않았다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.JoinTable;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Setter
@Getter
@Entity
@Table(name = "role")
public class Role {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column
private String name;
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(name = "users_roles",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "role_id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "user_id")
)
private List<User> users;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Role [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
7 Repository 구현하기
7-1 JpaRespository를 사용하여 구현한다.
7-2 CustomerRepository 인터페이스이다.
7-3 finAll과 별개로 검색 기능을 위해 search 메소드를 추가하였다. @Query는 아래 참조
Spring : Data JPA - @Query 사용하기
Spring Data JPA를 사용하다 보면 쿼리를 직접 사용할 경우가 있다. 1. 대부분의 경우 JpaRepository를 상속한 인터페이스를 정의하여 사용한다. 2. 사용자가 직접 query를 사용하고 싶으면 인터페이스에 ��
kogle.tistory.com
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.repository;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity.Customer;
public interface CustomerRepository extends JpaRepository<Customer, Long>{
@Query("from Customer where firstName LIKE CONCAT('%',:keyword,'%')")
List<Customer> search(@Param("keyword")String keyword);
}
7-3 UserRepository 인터페이스이다.
7-3-1 UserDetailsService는 id가 아닌 사용자이름으로 검색하기 때문에 별도의 메소드 생성이 필요하다.
7-3-2 아래는 메소드는 username으로 User를 찾는 간단한 메소드이다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity.User;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
@Query(value = "from User where username=:username")
User findByUsername(@Param("username") String username);
}
7-4 RoleRepository 인터페이스이다.
7-4-1 Role역시 이름으로 검색하는 메소드가 필요하므로 추가로 생성하였다.
7-4-2 회원가입시 기본 권한을 부여할 때 권한명을 사용한 검색이 필요하다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity.Role;
public interface RoleRepository extends JpaRepository<Role, Long> {
@Query("from Role where name=:name")
Role findbyName(@Param("name") String name);
}
8. 서비스 구현하기
8-1 CustomerService 인터페이스
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.service;
import java.util.List;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity.Customer;
public interface CustomerService {
List<Customer> getCustomers();
Customer getCustomer(Long id);
void saveCustomer(Customer customer);
void deleteCustomer(Long id);
}
8-2 CustomerServiceImpl 클래스
8-2-1 이 서비스는 두 개 이상의 entity를 사용하지 않기 때문에 @Transactional이 필요없다.
8-2-2 Spring Data가 Repository단에 자동으로 @Transactional을 부여한다.
8-2-3 getCustomers에 keyword를 받는데 값의 존재 유무에 따라 검색인지 전체 반환인지 결정한다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity.Customer;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.repository.CustomerRepository;
@Service
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
@Autowired
private CustomerRepository customerRepository;
@Override
public List<Customer> getCustomers(String keyword) {
if (keyword == null || keyword.length() == 0) {
return this.customerRepository.findAll();
} else {
return this.customerRepository.search(keyword);
}
}
@Override
public Customer getCustomer(Long id) {
Optional<Customer> customer = this.customerRepository.findById(id);
if (customer.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("user not found");
}
return customer.get();
}
@Override
public void saveCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customerRepository.save(customer);
}
@Override
public void deleteCustomer(Long id) {
Customer customer = this.getCustomer(id);
this.customerRepository.delete(customer);
}
}
8-3 UserService 인터페이스
8-3-1 유저 로그인을 위한 정보를 제공하기 위해 UserDetailsService를 상속하고 있다.
8-3-2 회원 가입시에 사용할 DTO를 수신하는 저장 메소드를 설정하였다.
8-3-3 주의 해야 할 부분은 이 인터페이스의 findUserByUsername메소드가 있다.
8-3-3-1 UserDetailsService에서 제공하는 loadUserByUsername 메소드와 혼동할 수 있는데, 약간 이름이 다르다.
8-3-3-2 여기서 이 메소드를 만든 이유는 회원가입시 클라이언트에서 로그인 확인을 위해 사용한다.
8-3-3-3 클라이언트는 username만 담아서 요청하고 서버는 그 사용자에 대한 정보를 반환한다.
8-3-3-4 반환될 유저정보에 비밀번호는 BCrypt된 것이라 실제 비밀번호를 알 수 없지만 나머지는 text정보이다.
8-3-3-5 실제 서비스에는 개인정보보호를 위해 전송전에 암호화 하는 것이 필요하다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.service;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.dto.UserDTO;
public interface UserService extends UserDetailsService {
void save(UserDTO userDTO);
UserDTO findUserByUsername(String username);
}
8-4 UserSerivceImpl 클래스
8-4-0 가장 중요한 클래스이다.
8-4-1 주의할 점은 Recursive구조가 안 생기도록 작성하는 것이다.
8-4-1-1 클라이언트와 통신할 Json으로 매핑될 객체에는 재귀가 생기는 객체들을 사용할 수 없다.
8-4-1-2 UserDTO를 생성한 이유이다.
8-4-2 로그인 데이터를 DaoAuthenticationProvider에 제공하기 위해 UserDetailsService를 구현한다.
8-4-2-1 이 메소드는 두 개 이상의 entity를 사용하므로 서비스 단에 @Transactional이 필수적이다.
8-4-2-2 User의 정보를 가져왔을 때 참조하고 있는 Role entity가 있는데 이것을 읽으려면 Session이 필요하다.
8-4-2-3 서비스 단에서 이 role을 읽고 있으므로 서비스 단까지 Transaction의 범위가 넓어져야 하는 것이다.
8-4-3 회원가입정보를 처리하는 save 메소드가 있다.
8-4-3-2 저장 후에 DTO에 id를 설정해야 클라이언트에게 생성한 유저정보에 id를 포함할 수 있다.
8-4-4 findUserByUsername도 외부로 전달하기 위해 UserDTO를 사용한다.
8-4-5 회원 가입 시 사용하는 save 메소드에서 중복이 발생할 때 처리하기 위해 별도의 예외클래스를 생성했다.
8-4-6 서버 사용자 인증을 제외한 모든 예외는 @ControllerAvice에서 처리한다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.service;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import javax.transaction.Transactional;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.dto.UserDTO;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity.Role;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity.User;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.error.DuplicatedUsernameException;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.repository.RoleRepository;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.repository.UserRepository;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserServiceImpl.class);
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
private RoleRepository roleRepository;
@Autowired
private BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
@Transactional
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userRepository.findByUsername(username);
if (user == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("user not found");
}
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(),
user.getRoles().stream().map(role-> new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getName())).collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Override
public void save(UserDTO userDTO) {
System.out.println("sever UserService save");
User fetchedUser = this.userRepository.findByUsername(userDTO.getUsername());
if (fetchedUser != null) {
System.out.println("Duplicated :: " + fetchedUser.toString() );
throw new DuplicatedUsernameException("username already taken");
}
User user = new User();
user.setId(userDTO.getId());
user.setUsername(userDTO.getUsername());
user.setPassword(this.passwordEncoder.encode(userDTO.getPassword()));
user.setFirstName(userDTO.getFirstName());
user.setLastName(userDTO.getLastName());
user.setEmail(userDTO.getEmail());
Role role = this.roleRepository.findbyName("ROLE_EMPLOYEE");
user.setRoles(Arrays.asList(role));
userDTO.setRoles(Arrays.asList(role.getName()));
LOGGER.debug(user.toString());
this.userRepository.save(user);
System.out.println(user.toString());
userDTO.setId(user.getId());
}
@Override
@Transactional
public UserDTO findUserByUsername(String username) {
User user = this.userRepository.findByUsername(username);
if (user == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("user not found");
}
UserDTO userDTO = new UserDTO();
userDTO.setId(user.getId());
userDTO.setUsername(user.getUsername());
userDTO.setPassword(user.getPassword());
userDTO.setFirstName(user.getFirstName());
userDTO.setLastName(user.getLastName());
userDTO.setEmail(user.getEmail());
userDTO.setRoles(user.getRoles().stream().map(role-> role.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
return userDTO;
}
}
9. 예외처리하기
9-1 예외처리는 한 곳에서 하는 것이 효율적이므로 예외 처리 클래스를 별도로 생성한다.
9-1-0 예외처리를 위해서 예외정보를 담을 클래스를 생성한다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.error;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class CustomerErrorResponse {
private int statusCode;
private String message;
private long timestamp;
}
9-1-1 입력 타입이 맞지 않았을 때, 중복된 유저이름으로 회원가입을 시도할 때, 사용자를 못찾았을 때
9-1-2 예외처리를 하고 있는 예외처리 클래스이다. 필요한 경우 처리할 예외를 추가하여 확장할 수 있다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.error;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.method.annotation.MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException;
@ControllerAdvice
public class CustomerExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<CustomerErrorResponse> processError(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception");
CustomerErrorResponse response = new CustomerErrorResponse();
HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND;
if (e instanceof MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException) {
status = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
response.setStatusCode(status.value());
response.setMessage("Only number is allowed");
} else if (e instanceof DuplicatedUsernameException) {
status = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
response.setStatusCode(status.value());
response.setMessage(e.getMessage());
} else {
status = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND;
response.setStatusCode(status.value());
response.setMessage(e.getMessage());
}
response.setTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
return new ResponseEntity<>(response, status);
}
}
9-2 UserService에서 발생시킨 중복 username에 대한 예외클래스
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.error;
public class DuplicatedUsernameException extends RuntimeException {
public DuplicatedUsernameException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public DuplicatedUsernameException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public DuplicatedUsernameException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
10 Controller 작성하기
10-0 모든 End Point를 ResponseEntity로 처리하는 것이 좋지만, 아래의 경우는 필요한 경우에만 그렇게 했다.
10-1 CustomerController클래스이다. 예전과 다른 점이 없다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.entity.Customer;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.service.CustomerService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class CustomerController {
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@GetMapping("/customers")
public List<Customer> getCustomers() {
System.out.println("Get Customers :: ");
return this.customerService.getCustomers();
}
@GetMapping("/customers/{id}")
public Customer getCustomer(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return this.customerService.getCustomer(id);
}
@PostMapping("/customers")
public Customer addCustomer(@RequestBody Customer customer) {
System.out.println("Post :: " + customer.toString());
this.customerService.saveCustomer(customer);
return customer;
}
@PutMapping("/customers")
public Customer updateCustomer(@RequestBody Customer customer) {
System.out.println("Put :: " + customer.toString());
this.customerService.saveCustomer(customer);
return customer;
}
@DeleteMapping("/customers/{id}")
public void deleteCustomer(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
this.customerService.deleteCustomer(id);
}
}
10-2 UserController 클래스
10-2-1 회원가입을 위한 /user uri의 register메소드는 UserDTO를 사용하고 있고 결과도 UserDTO를 담는다.
10-2-2 클라이언트의 로그인 지원을 위한 login메소드가 있다. 이 login은 서버 로그인하고 아무런 상관이 없다.
10-2-2-1 즉 서버는 stateless이기 때문에 session이 없다. 즉 login을 해서 클라이언트에서 관리해야 한다.
package pe.pilseong.crmserver.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.dto.UserDTO;
import pe.pilseong.crmserver.service.UserService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping("/login")
public UserDTO login(@RequestBody UserDTO user) {
System.out.println("Login attmpted :: " + user);
UserDTO userDTO = this.userService.findUserByUsername(user.getUsername());
return userDTO;
}
@PostMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity<UserDTO> register(@RequestBody UserDTO user) {
this.userService.save(user);
return new ResponseEntity<UserDTO>(user, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
}
'Spring > Spring Advanced' 카테고리의 다른 글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 도커 개발환경 참고
- AWS ARN 구조
- Immuability에 관한 설명
- 자바스크립트 멀티 비동기 함수 호출 참고
- WSDL 참고
- SOAP 컨슈머 참고
- MySql dump 사용법
- AWS Lambda with Addon
- NFC 드라이버 linux 설치
- electron IPC
- mifare classic 강의
- go module 관련 상세한 정보
- C 메모리 찍어보기
- C++ Addon 마이그레이션
- JAX WS Header 관련 stackoverflow
- SOAP Custom Header 설정 참고
- SOAP Custom Header
- SOAP BindingProvider
- dispatcher 사용하여 설정
- vagrant kvm으로 사용하기
- git fork, pull request to the …
- vagrant libvirt bridge network
- python, js의 async, await의 차이
- go JSON struct 생성
- Netflix Kinesis 활용 분석
- docker credential problem
- private subnet에서 outbound IP 확…
- 안드로이드 coroutine
- kotlin with, apply, also 등
- 안드로이드 초기로딩이 안되는 경우
- navigation 데이터 보내기
- 레이스 컨디션 navController
- raylib
- MYSQL
- 외부파일
- Rest
- crud
- Spring
- 설정하기
- one-to-one
- jsp
- hibernate
- XML
- RestTemplate
- Security
- Validation
- WebMvc
- 자바
- Many-To-Many
- 로그인
- 스프링
- spring boot
- Angular
- mapping
- Spring Security
- 매핑
- 상속
- 설정
- 하이버네이트
- one-to-many
- form
- login
- 스프링부트
